Teradata was once a popular and preferred analytics platform. But its inability to provide complex analytical features necessary for the current business environment and high licensing costs, are some of the most significant reasons for Teradata migration. A switch is deemed necessary by organizations to efficiently capture these changes and move to an environment that better caters to their dynamic business needs.
But migrating from Teradata involves many challenges. While every business has its own plan for migration, there are many pitfalls that can lead to an unsuccessful migration, compatibility issues with the new system, or even loss of data. Based on our years of experience in cloud migration, we’ve identified a few mistakes that most businesses make, and how you can avoid them for a successful migration.
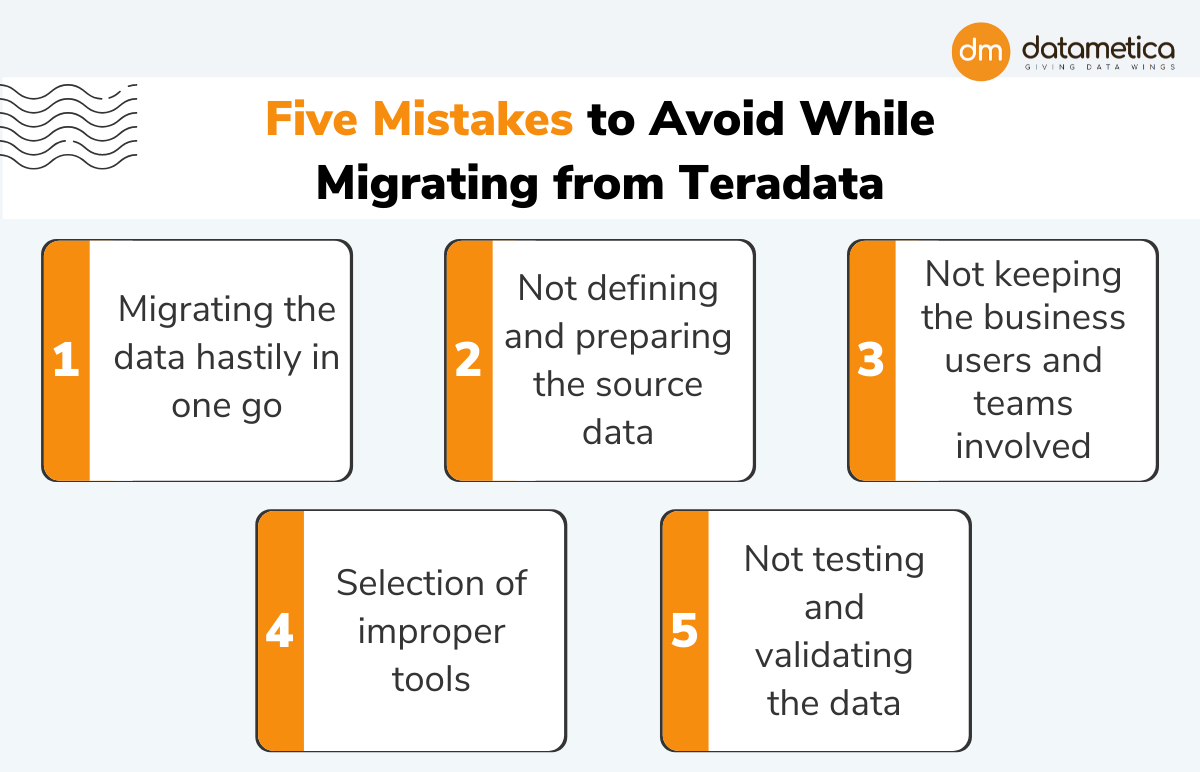
Mistake 1: Migrating the data hastily in one go
Effective data migration needs proper planning, similar to the execution of any big project.
Despite the pressure to migrate data in the shortest time possible, allocating sufficient planning time is critical to fully understand a complex Teradata Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW). Planning makes the migration process smoother and avoids disruption of business operations.
Engaging an experienced data migration partner helps reduce the risk associated with the project. A phased method of migration that offloads critical workloads in steps will reduce the risk of an expensive failure while ensuring better time-to-value by avoiding a migration riddled with technical challenges and coming to a complete halt.
At this stage, an automated data warehouse assessment tool would be of great help to the organization as it provides a clear idea of the project’s complexity and potential future obstacles.
Mistake 2: Not defining and preparing the source data
It is essential to define what source data will be moved in the initial stages of migration and thoroughly examine the data. Critical failures can result even from overlooking gaps, errors, duplicates, and misspellings in the source data as you try to modify or configure the source data to fit new parameters.
It’s important to clean the source data before the process – and not midway – and to identify by which method the data is categorized. As a positive side benefit, migration is also an excellent opportunity for organizations to eliminate any legacy structures that are obsolete for users and weed out inefficiencies.
Suggested read: How Datametica helped a retailer migrate from Teradata to GCP and achieve a 55% reduction in overall costs and 60% reduction in query execution time.
Mistake 3: Not keeping the business users and teams involved
Communication is critical during migration; it is important for the migration team to extensively discuss the process and its implication with all relevant departments in the organization before initiating the process. The IT department may be responsible for data integrity post-migration, but business units are the end-users of data. Communication with them helps highlight apps and workflows that were thought to be obsolete but are critical to business.
By not involving them and not taking their feedback on cleansing, merging, or restructuring the data they use every day, the IT team might get flooded with support requests after the migration.
Mistake 4: Selection of improper tools
Migration from Teradata first requires understanding the EDW to finalize components to migrate, translate code, and then migrate to the destination. Conventionally, it involves enormous volumes of SQL, SP, DDLs, Bteq code, etc, and doing it manually is highly inefficient and resource-intensive. Selecting proper tools for data warehouse assessment, code translation, and data validation streamlines the migration process, causing fewer disruptions to processes and helping save time and money.
Successful Teradata migration demands automating specific functions. Migration automation tools survey the EDW in a short timeframe, translate the code, and allow developers to work on edge cases and outliers.
Mistake 5: Not testing and validating the data
Many businesses think that a migration process is completed after the data is transferred to the destination system. However, it’s far from thorough; effective testing must ensure that all the data has been migrated accurately. An effective automated data validation tool helps match the data on the new cloud platform and legacy system.
Validating the data is as critical a step as migrating since it assures the team that all the data has been migrated correctly and will work as expected to yield accurate results.
Conclusion
The journey of migration from Teradata becomes easier when an action plan is formulated with proper planning and avoiding the common pitfalls. To ensure a successful migration, it is best recommended to partner with an experienced migration team.
Datametica is a global leader in data warehouse modernization and migration and has helped many businesses migrate to the cloud with a state-of-the-art migration automation suite. Reach out to our experts to know more.
.
.
.
About Datametica
A Global Leader in Data Warehouse Modernization & Migration. We empower businesses by migrating their Data/Workload/ETL/Analytics to the Cloud by leveraging Automation.